In today’s rapidly evolving world, sustainability has become a crucial concept for businesses, governments, and individuals alike. But what exactly does it mean, and why is it so important? Sustainability refers to the ability to maintain or support processes over time, particularly those that conserve resources and protect the environment. As we face increasing concerns about climate change, pollution, and resource depletion, the focus on sustainable development has never been more significant.
What is Sustainability?
Sustainability encompasses practices that ensure the long-term viability of resources and ecosystems. In business and policy, sustainability is about preventing the depletion of natural resources to ensure they are available for future generations. This approach is closely linked to the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), which provide a framework for global efforts to achieve a more sustainable future.
Key Takeaways
- Sustainability is about maintaining processes over time.
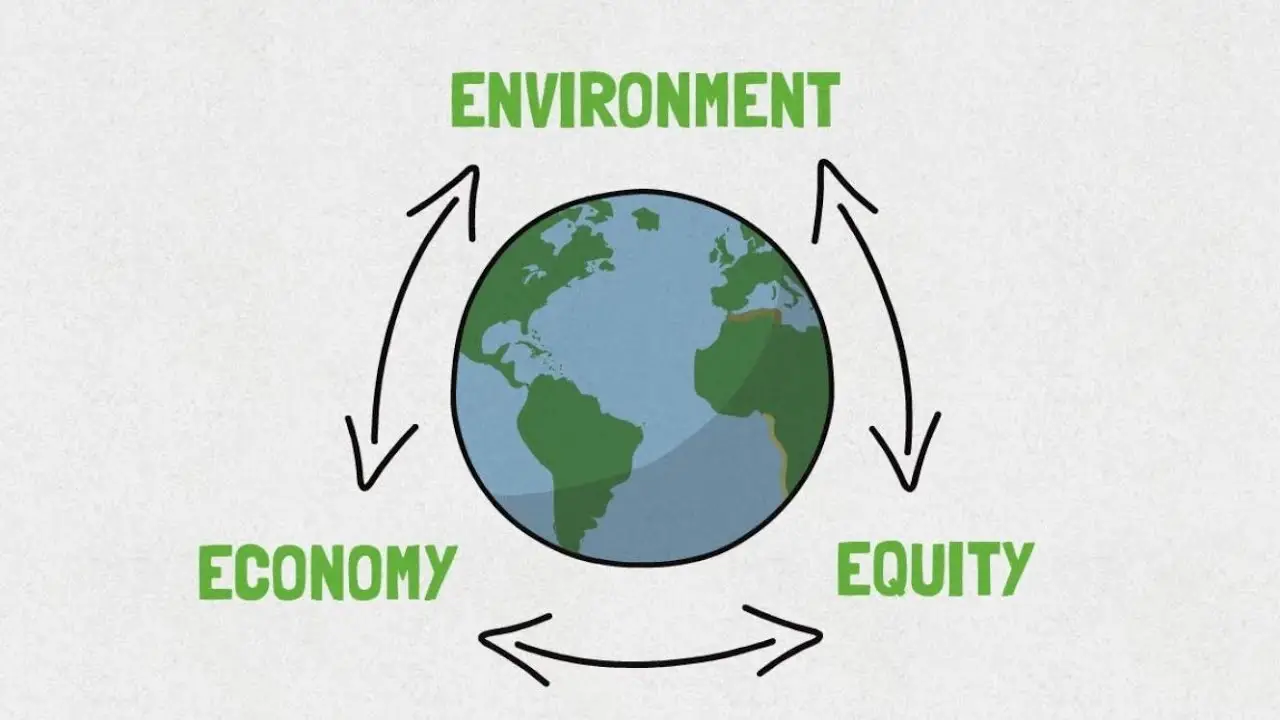
- It includes three core pillars: economic, environmental, and social sustainability.
- Businesses and governments are increasingly committed to sustainable development.
- Green investments and sustainable practices are gaining popularity among investors.
- Skeptics warn against “greenwashing,” where companies falsely portray themselves as environmentally friendly.
How Sustainability Works
Sustainable policies focus on the long-term effects of practices on humans, ecosystems, and the broader economy. The belief is that without major changes, our planet will suffer irreparable damage. This belief has led to a global shift towards sustainability, primarily through sustainable business practices and investments in green technology.
The 3 Pillars of Sustainability
Sustainability is often broken down into three pillars: economic, environmental, and social. These are sometimes referred to as profits, planet, and people.
- Economic Sustainability: Focuses on conserving natural resources essential for economic production. This includes both renewable and exhaustible resources.
- Environmental Sustainability: Emphasizes maintaining life support systems like the atmosphere and soil, which are critical for economic production and human life.
- Social Sustainability: Addresses the human impact of economic systems, including efforts to eradicate poverty, hunger, and inequality.
The United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) are a key part of this framework, offering a blueprint for achieving sustainability globally.
Corporate Sustainability
In business, sustainability goes beyond environmentalism. It involves practices that positively impact both society and the environment. Corporate sustainability emerged in response to public concerns about the long-term damage caused by focusing solely on short-term profits.
Measuring Corporate Sustainability
Harvard Business School suggests measuring corporate sustainability by evaluating a company’s impact on the environment and society. Sustainable practices may include reducing emissions, lowering energy usage, sourcing from fair-trade organizations, and minimizing waste. Many companies have set ambitious sustainability goals, such as achieving zero emissions or reducing their overall environmental impact by a specific year.
Real-World Examples
Several corporations have made notable sustainability commitments. For example:
- Walmart aims to achieve zero emissions by 2040.
- Google plans to operate carbon-free by 2030.
- Morgan Stanley has pledged net-zero “financed emissions” by 2050.
These companies are leading the way in sustainability, but some have faced accusations of greenwashing, where they exaggerate their environmental efforts.
Challenges Surrounding Business Sustainability
While sustainability is desirable, it is not always easy to achieve. Several challenges can impede the adoption of sustainable practices:
- Understanding Impact: It can be difficult for companies to fully understand their environmental impact.
- Ranking Environmental Impact: Determining the relative environmental impact of different activities is complex.
- Predicting Responses: Predicting how economic agents will respond to changes in sustainability incentives is challenging.
Despite these challenges, the demand for sustainable investing continues to grow. Surveys suggest that many investors consider sustainability fundamental to their investment strategies.
Benefits of Business Sustainability
Implementing sustainability strategies offers numerous benefits, both social and financial. Environmentally conscious practices can improve a company’s long-term viability, reduce costs, and enhance its public image. For instance, using energy-efficient lighting can save money on utility bills and boost a company’s appeal to eco-conscious consumers.
Sustainability can also make a company more attractive to investors. Research shows that shareholders value the ethical dimensions of a business, and companies with strong sustainability practices often enjoy higher valuations.
Creating a Sustainable Business Strategy
Many companies are integrating sustainability into their core business models. To do this effectively, they must follow several key steps:
- Identify Weaknesses: Companies should start by identifying areas where they need improvement, such as reducing waste or enhancing diversity.
- Set Goals: Companies should establish clear, measurable sustainability goals, such as reducing their carbon footprint or increasing diversity in hiring.
- Implement and Assess: The final step is to implement the strategy and continually assess its effectiveness, making adjustments as needed.
Common Pitfalls in Pursuing Sustainability
While sustainability is a noble goal, there are common pitfalls to avoid:
- Knowledge-Action Gap: Many companies set sustainability goals but fail to take concrete actions to achieve them.
- Compliance-Competitiveness Gap: Companies must distinguish between mandatory compliance and voluntary sustainability efforts. While sustainability can enhance competitiveness, it should not be confused with regulatory requirements.
Real-World Example: Unilever’s Sustainability Success
A successful example of a sustainability strategy is Unilever’s Sustainable Living Plan. Launched in 2010, this ten-year plan aimed to reduce the environmental impact of Unilever’s brands while promoting a fair workplace. By the end of the plan, Unilever had made significant strides, saving more than 1 billion euros by conserving water and energy and becoming the preferred employer for graduates in 50 countries.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What Are the 3 Principles of Sustainability?
The three principles of sustainability are environmental, social, and economic sustainability. These principles are often summarized as people, planet, and profits.
What Activities Promote Sustainability?
Sustainability can be promoted through activities like using renewable energy, reducing waste, and implementing fair labor practices. Sustainable businesses also focus on benefiting the local community.
What Is Economic Sustainability?
Economic sustainability refers to a company’s ability to continue its operations over the long term while ensuring adequate resources, workers, and consumers for its products.
What Are the Most Sustainable Companies?
The most sustainable companies are often ranked based on their commitment to environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria. Companies like Vestas Wind Systems, Autodesk Inc., and Schneider Electric are frequently recognized for their sustainability efforts.
What Products Are Not Sustainable?
Non-sustainable products are those that rely on resources that cannot be replaced at the same rate they are consumed. This includes products made from fossil fuels, rainforest timber, and other non-renewable resources.
Conclusion
As consumers become more environmentally conscious, sustainability has become a critical focus for companies and governments worldwide. By adopting sustainable practices and embracing the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), businesses can contribute to a more sustainable future while also improving their bottom line. Whether through reducing emissions, promoting fair labor practices, or investing in green technologies, the path to sustainability is not only beneficial but necessary for the long-term health of our planet and society.