Ever wonder how Netflix knows exactly what show you’ll love next? Or how Amazon suggests a product you didn’t even know you needed? The magic behind these smart recommendations is a powerful field called data science.
If you’ve heard the term but aren’t quite sure what it means, you’ve come to the right place. This guide will explain what is data science in simple words, how it affects your daily life, and why it’s one of the most exciting careers today.
So, What Is Data Science, Really?
In simple terms, data science is the art of understanding data. Think of a data scientist as a modern-day detective. They gather clues (data), look for patterns, and solve mysteries to help businesses and organizations make smarter choices.
The data science definition is the study of data to find useful insights. It’s a mix of different skills, including math, computer science, and business knowledge. By using special tools and their creativity, data scientists can look at huge amounts of messy information and pull out valuable secrets that were hidden inside.
These secrets can help answer important questions, like:
- What do our customers really want?
- How can we make our services better?
- What products will be popular next holiday season?
- How can we spot problems before they happen?
Ultimately, data science is about turning raw information into useful knowledge that helps us make better decisions.
How Data Science Works: The Detective’s Process
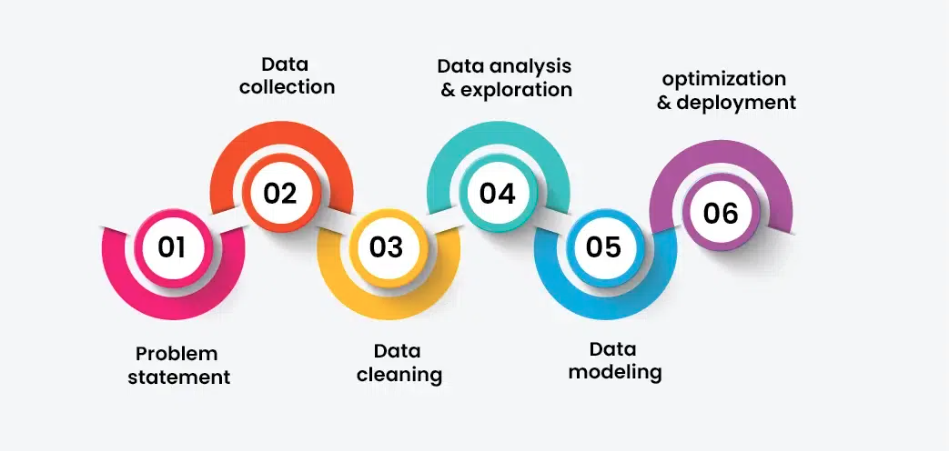
To solve a mystery, a detective follows a series of steps. A data scientist does something very similar. The data science process usually involves these key stages:
Step 1: Gathering the Clues (Data Collection)
First, a data scientist needs data. This information is collected from many different places. It could be customer surveys, website clicks, sales records, social media posts, sensor readings, or even images and videos. The goal is to gather all the relevant clues.
Step 2: Cleaning Up the Evidence (Data Cleaning)
Raw data is almost always messy. It can have mistakes, missing pieces, or information that just doesn’t make sense. In this step, the data scientist “cleans” the data. They fix errors, fill in gaps, and remove irrelevant information to make sure the data is accurate and ready for analysis. This is a critical step, as bad data leads to bad conclusions.
Step 3: Finding the Patterns (Data Analysis)
This is where the real investigation begins. Using tools from statistics and computer programming, the data scientist starts looking for trends, patterns, and connections within the data. Are sales of ice cream going up when the weather gets warmer? Do customers who buy one product often buy another? This analysis helps turn numbers into a story.
Step 4: Telling the Story (Data Visualization)
Finding an important clue is great, but it’s not helpful if you can’t explain it to others. Data scientists use charts, graphs, and dashboards to present their findings in a way that is easy for everyone to understand. This is called data visualization, and it helps turn complex findings into clear, actionable insights.
Step 5: Making a Smart Decision (Decision-Making)
The final step is to use these insights to make a real-world decision. The business might launch a new marketing campaign, change a product feature, or optimize its supply chain based on what the data revealed. This is how data science creates real value.
Why Is Data Science So Important?
In today’s world, we create an enormous amount of data every single second. Data science is the key to unlocking the power of that data. Here’s why it’s so crucial for almost every industry.
- Better Business Decisions: Instead of guessing, businesses can use data to make choices that are more likely to succeed. This reduces risks and helps increase profits.
- Making Things More Efficient: Data science can spot bottlenecks in a process. For example, it can help a factory figure out why a machine keeps breaking down or help a delivery company find the fastest routes, saving time and money.
- Creating Personalized Experiences: It’s the reason your Spotify Discover Weekly playlist feels like it was made just for you. Data science helps companies understand your personal tastes and provide customized content, products, and ads.
- Predicting the Future: By analyzing past trends, data science can help forecast future events. Businesses can predict how much of a product they will sell, and hospitals can predict when a flu season might be severe.
- Driving New Ideas and Innovation: Sometimes, data reveals a surprising insight that leads to a brand-new product or service. Many of today’s tech innovations, like self-driving cars, are powered by data science.
- Helping Society: Data science isn’t just for businesses. It helps improve public services by making healthcare more effective, transportation systems smarter, and education more personalized for students.
Real-Life Examples of Data Science You See Every Day
You interact with the results of data science all the time, probably without even realizing it. Here are some clear, real-life examples that show how data science helps shape our world.
Your Streaming and Social Media Feeds

Have you ever binged a show on Netflix and then seen dozens of similar recommendations pop up? Or scrolled through your Instagram or TikTok feed and felt like it knew exactly what you wanted to see?
- How it Works: These platforms use data science to analyze everything you do: what you watch, what you “like,” what you comment on, how long you watch a video, and what you search for. Their algorithms (special sets of computer rules) process this data to create a personalized feed designed to keep you engaged.
Your Online Shopping Experience
E-commerce giants like Amazon and Flipkart are masters of data science. They use it to transform your shopping journey.
- How it Works: They track your browsing history, what you put in your cart, your past purchases, and even what other shoppers like you are buying. This data powers the “Frequently Bought Together” and “Customers who viewed this item also viewed” sections. It also helps them forecast demand, so they know how many of a certain item to keep in their warehouses for an upcoming holiday.
Healthcare and Early Disease Detection
Data science is making incredible advances in medicine. It’s helping doctors save lives by catching illnesses earlier than ever before.
- How it Works: By analyzing a patient’s medical records, genetic information, and lifestyle habits, data science models can predict their risk for diseases like diabetes or heart disease. It can also analyze medical images, like X-rays or MRIs, to help doctors spot tiny signs of tumors or other conditions at a very early stage, when treatment is most effective.
Finding the Fastest Route with GPS
If you use Google Maps or Waze, you are using data science. These apps don’t just show you a map; they tell you the best way to get to your destination right now.
- How it Works: These apps collect real-time traffic data from thousands of other users on the road. Data science algorithms analyze this flow of information to identify traffic jams, accidents, and road closures. They then calculate the fastest route for you and can even reroute you if conditions change while you’re driving.
Which Industries Use Data Science?
The short answer? Almost all of them! Data science is transforming how work gets done across many different fields.
- Healthcare: For predicting diseases, creating personalized treatments, and making hospitals run more smoothly.
- Finance: To detect credit card fraud, manage financial risk, and offer personalized investment advice.
- Retail: To understand what customers want, manage inventory, and create targeted marketing campaigns.
- Technology: Data science is the engine behind search engines, virtual assistants (like Siri and Alexa), and many AI innovations.
- Transportation: To optimize delivery routes, manage traffic, and perform predictive maintenance on vehicles.
- Manufacturing: To predict when equipment might fail, improve production lines, and manage the supply chain.
- Entertainment: To recommend movies and music, analyze audience preferences, and decide what new content to create.
- Agriculture: To help farmers grow more food by monitoring crop health, managing water usage, and optimizing planting schedules (a field known as precision farming).
Who Is a Data Scientist and What Skills Do They Need?
So, who are the people doing all this amazing work? They are called data scientists. A what is data scientist definition is a professional who uses their technical and analytical skills to extract meaningful insights from data. They are part detective, part statistician, and part computer scientist.
To become a successful data scientist, a person needs a unique mix of skills:
Technical Skills
- Programming: You need to speak the language of computers. Languages like Python and R are very popular for data analysis. SQL is also essential for getting data from databases.
- Statistics and Math: A strong foundation in math is key to understanding the patterns in data and knowing which methods to use.
- Machine Learning: This is a type of AI that allows computers to learn from data without being explicitly programmed. It’s used to build predictive models, like the ones that power recommendation engines.
- Data Visualization: The ability to use tools like Tableau or Power BI to create charts and graphs that make data easy to understand.
- Big Data Tools: Experience with technologies like Hadoop or Spark, which are designed to handle massive datasets that are too large for a regular computer.
Soft Skills
- Critical Thinking: The ability to ask the right questions, look at problems from different angles, and find creative solutions.
- Communication: A data scientist must be able to explain their complex findings in a simple, clear way to people who are not experts, like business leaders.
- Curiosity: A deep desire to explore data and uncover what it has to say is one of the most important traits of a great data scientist.
How Can Someone Learn Data Science?
With the demand for data scientists booming, many people are interested in this career. If you’re wondering what is a data science course and how to get started, here’s a general path:
- Build a Strong Foundation: Start by learning the basics of math, statistics, and programming. There are countless free and paid online courses on platforms like Coursera, edX, and Khan Academy.
- Learn Key Programming Languages: Focus on learning Python or R, as they are the industry standards.
- Dive into Machine Learning: Once you have the basics down, start learning about machine learning algorithms and how to apply them.
- Practice with Real Projects: The best way to learn is by doing. Find interesting datasets online (sites like Kaggle are great for this) and work on your own projects. Try to predict something, classify information, or create an interesting visualization.
- Learn Visualization Tools: Get comfortable with a tool like Tableau or Power BI to learn how to present your findings professionally.
- Stay Updated: Data science is a fast-moving field. Keep learning by reading blogs, joining online communities, and following experts in the field.
Common Jobs in the World of Data Science
The term “data science” covers a variety of roles. Here are some of the most common jobs you’ll find:
- Data Scientist: The “all-rounder” who analyzes data, builds models, and communicates insights to help with business strategy.
- Data Analyst: Focuses on collecting, cleaning, and analyzing data to find trends. They often create reports and dashboards to share their findings.
- Data Engineer: The “plumber” of the data world. They build and maintain the systems (called data pipelines) that collect and store large amounts of data, ensuring it’s ready for scientists and analysts to use.
- Machine Learning Engineer: A specialist who focuses on building and deploying machine learning models and putting them into production.
- Business Intelligence (BI) Analyst: Connects the data world with the business world. They use data to create reports that help leaders track performance and make strategic decisions.
- Data Architect: The designer of the company’s entire data system. They plan how data will be stored, managed, and secured.
Data science is more than just a buzzword. It’s a revolutionary field that is using the power of information to solve complex problems, drive innovation, and make our world smarter and more efficient. The next time your favorite app gives you a perfect recommendation, you’ll know it’s not magic—it’s data science at work.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational and educational purposes only. The content is intended to provide a general overview of data science and should not be considered professional, medical, financial, or legal advice. Always consult with a qualified professional for specific advice related to your situation.
![What Is Data Science? [2025/2026] A Simple Guide for Everyone What Is Data Science? [2025/2026] A Simple Guide for Everyone](https://topindiatips.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/data-science-xe1pmo7wm4jcokpd.webp)